 |



The concentration of chlorate in the saltwater entering the tank will reduce the quality of caustic soda products, corrode equipment pipelines, and shorten equipment life. The production of chlorates cannot be separated from the migration of alkali to the anode chamber, and the pinholes or damages on the ion membrane provide channels for the penetration of alkali from the cathode chamber to the anode chamber. Adding acid to the anode chamber or repairing and replacing the ion membrane can reduce chlorate enrichment. The more commonly used method in actual production is to use a chlorate decomposition tank.
Temperature, acid dosage, amount of diluted salt water entering the decomposition tank, and chlorate content all have an impact on the effectiveness of the chlorate decomposition tank. When the content of chlorate is high, hydrochloric acid needs to be added to the diluted salt water. The hydrochloric acid online analyzer is used to detect the amount of hydrochloric acid added online, which can guide the amount of hydrochloric acid added to avoid waste.
Analysis principle
The analyzer collects electrode potential to determine the volume of standard titration solution at the endpoint, thereby determining the content of hydrochloric acid in the saline solution. Potentiometric titration is a method of determining the endpoint of titration by measuring changes in potential during the titration process. Compared with direct potentiometry, potentiometric titration does not require accurate measurement of electrode potential values. Therefore, the influence of temperature and liquid junction potential is not important, and its accuracy is better than direct potentiometry. Conventional titration relies on changes in indicator color to indicate the endpoint of titration. If the solution to be tested has color or turbidity, it is difficult to indicate the endpoint, or suitable indicators cannot be found at all. Potentiometric titration relies on the sudden jump of electrode potential to indicate the endpoint of titration. Before and after reaching the endpoint of titration, the concentration of the analyte in the droplet often changes continuously by n orders of magnitude, causing a sudden jump in potential. The content of the analyte is still calculated by the amount of titrant consumed. During the titration process, as the titrant is continuously added, the electrode potential E changes continuously. When the electrode potential suddenly jumps, it indicates that the titration has reached the endpoint. It is easier to determine the titration endpoint using a differential curve than a regular titration curve.
Product parameters (installed at the outlet of NaCl O3 decomposition tank)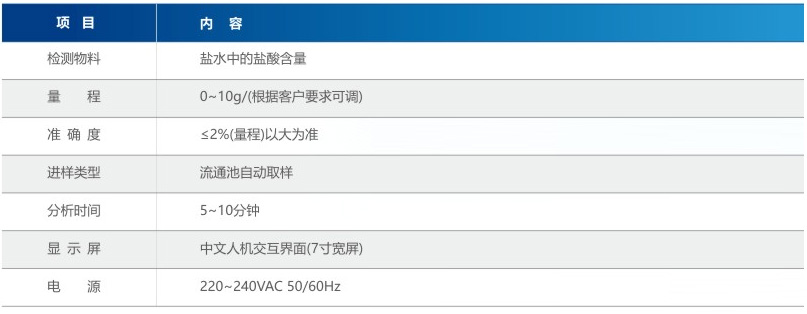

RJ(SZ)Technology Co., Ltd.
RJ(SZ) Operation and Maintenance Center
Shenzhen Headquarters: 2048, Silicon Bay Chip Design Center, No.1 Jingang Road, Wanggang Avenue, Shajing Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen
Contact phone number: 18124079712
Kaiming KMW Water Quality Monitor Channel Cooperation Contact Number: 13828819385

Runjin Huanke WeChat official account

Channel distributors, please scan the code for consultation